In our previous article, we learned that a large percentage of infertility can be attributed to either male or female factors, or a combination of both.
- One-third of infertility cases are caused by male factor infertility.
- One-third of infertility cases are caused by female factor infertility.
- One-third of infertility cases are caused by a combination of male and female factor infertility, or have unknown causes.
How Pregnancy Occurs
To get a better grasp of infertility, it’s important to learn the basic process of conception, and the male and female factors that play a huge role in it. The requirements for natural conception are as follows:
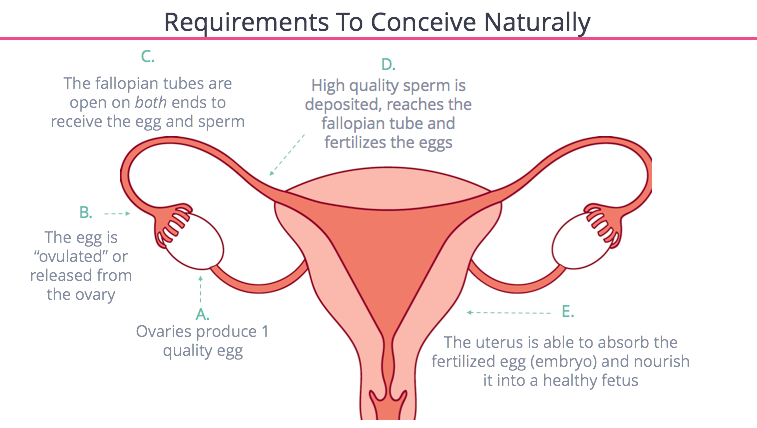
(Source: FertilityIQ)
Pregnancy occurs in four main stages: Ovulation, Fertilization, Transportation and Implantation.
First, a woman needs to produce a quality egg (ovulation). During sex, a man releases sperm, which travels to the fallopian tube to join with the egg (fertilization). The fertilized egg then travels down to the uterus (transportation) and attaches to the uterus (implantation). Pregnancy occurs if the implantation is successful.
Anything that hinders any of the conception stages can prevent pregnancy.
Causes of Female Infertility
The most common causes of infertility in women include:
- Ovulation problems – In 25% of infertility cases, ovulation problems are pinpointed as the main culprit. Such issues have varying sources, the most common being polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that causes irregular or absent periods. Other causes of ovulation problems include stress, obesity or being underweight, excessive exercise, and medical conditions such as perimenopause, premature ovarian failure, hyperprolactinemia and thyroid dysfunction.
- Endometriosis – This condition occurs when endometrium or uterine lining becomes displaced and develops outside the uterus, usually growing in pelvic organs such as the ovaries and the fallopian tubes. Endometriosis can cause scarring in the ovaries and fallopian tubes, preventing egg release. The condition can also affect egg quality and block the fallopian tubes, preventing sperm from fertilizing the egg.
- Blocked fallopian tubes – Blockage to the fallopian tube prevents sperm from fertilizing the egg. Similarly, damages, scars and adhesions in the tubes prevent a mature egg from being released to the fallopian tubes where fertilization normally occurs.
- Uterine fibroids – Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus, varying in size, number and location. Uterine fibroids are not a primary cause of infertility. However, fibroids that are too large can alter the shapes of the cervix and uterus, thereby affecting the number of sperm that enters the womb and the ability of an embryo to implant itself. In some cases, fibroids may cause blockage to the fallopian tubes.
- Premature ovarian failure or insufficiency – Also known as early menopause, this condition occurs when the ovaries suddenly stop working before the age of 40 to 50. This prevents eggs to be produced and released for fertilization.
Age – It is no secret that as a woman gets older, her fertility (egg quality and quantity) decreases.
Causes of Male Infertility
Meanwhile, the most common causes of infertility in men include:
- Abnormal sperm production – For pregnancy to happen, a man must produce quality sperm to fertilize a quality egg. However, genetics, poor lifestyle, environmental factors and medical conditions such as undescended testes, diabetes and STDs can cause low sperm count (oligospermia), zero sperm count (azoospermia), poor sperm motility, oddly-shaped sperm or underdeveloped sperm.
- Varicocele – This condition occurs when the veins in the scrotum become enlarged. These veins, called pampiniform plexus, keep the blood that flows to the testicular artery cool. When they become enlarged, the role of these veins is compromised, leading to high temperature levels in the testicles. This negatively affects sperm production, function and motility.
- Poor sperm delivery – Pregnancy cannot occur without fertilization. Blockage or damage in the testicles, injury to the male reproductive organs, and conditions such as cystic fibrosis and premature ejaculation prevents sperm from being released and travelling to the fallopian tubes to fertilize the egg.
- Hypogonadism – This is a male condition where not enough testosterone is produced, thereby resulting in low or zero sperm production.
- Environmental factors – Overexposure to heat, tobacco smoke, alcohol, radiation, pesticides and other chemicals are known to decrease male fertility. Steroids, and certain medicines and treatments like radiotherapy and chemotherapy can also affect sperm production.
Similar to women, age is also a contributing factor for infertility in men.
Infertility Treatments
As with all illnesses, treatment will depend on the diagnosed cause. With fertility, treatments range from simple lifestyle adjustments to medications. Hormonal therapy is typically recommended to address ovulation problems and improve testicular function. In some cases, surgery is required to restore fertility. Such procedures are typically reserved to address uterine fibroids, endometriosis and blockages in the fallopian tubes or testicles.
In other cases, assisted reproductive technology (ART) is an option. This is a modern and multidisciplinary approach to help couples conceive outside natural means. Techniques include:
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) – Mature eggs are harvested from stimulated ovaries, and fertilization is done outside the body in a laboratory dish. The fertilized egg will then be implanted into the uterus.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI) – Sperm is directly injected into the uterus to quicken the fertilization process.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) – A single sperm is directly injected into the mature egg.
- Zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT) – The fertilized egg (zygote) is placed in the fallopian tube.
- Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) – The eggs and sperm are directly placed in the fallopian tube for fertilization.
Other methods of ART include assisted hatching and the use of donor eggs and sperm.

Leave a comment